Bootstrapper - Application.cfc
The Application.cfc is one of the most important files in your application as it is where you define all the implicit ColdFusion engine events, session, client scopes, ORM, etc. It is also how you tell ColdFusion to bootstrap the ColdBox Platform for your application. There are two ways to bootstrap your application:
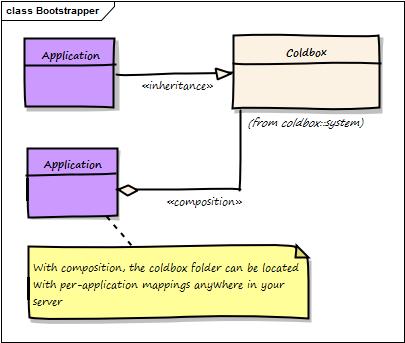
Leverage composition and bootstrap ColdBox (Default)
Leverage inheritance and bootstrap ColdBox
Tip: To see the difference, just open the appropriate Application.cfc in the application templates.
Composition
Inheritance
Directives
You can set some variables in the Application.cfc that can alter Bootstrapping conditions:
Variable
Default
Description
COLDBOX_APP_ROOT_PATH
App Directory
Automatically set for you. This path tells the framework what is the base root location of your application and where it should start looking for all the agreed upon conventions. You usualy will never change this, but you can.
COLDBOX_APP_MAPPING
/
The application mapping is ESSENTIAL when dealing with Flex or Remote (SOAP) applications. This is the location of the application from the root of the web root. So if your app is at the root, leave this setting blank. If your application is embedded in a sub-folder like MyApp, then this setting will be auto-calculated to /MyApp.
COLDBOX_CONFIG_FILE
config/ColdBox.cfc
The absolute or relative path to the configuration CFC file to load. This bypasses the conventions and uses the configuration file of your choice.
COLDBOX_APP_KEY
cbController
The name of the key the framework will store the application controller under in the application scope.
COLDBOX_FAIL_FAST
true
By default if an app is reiniting and a request hits it, we will fail fast with a message. This can be a boolean indicator or a closure.
Lock Timeout
The Boostrapper also leverages a default locking timeout of 30 seconds when doing loading operations. You can modify this timeout by calling the setLockTimeout() method on the Bootsrapper object.
Was this helpful?