Working with Events
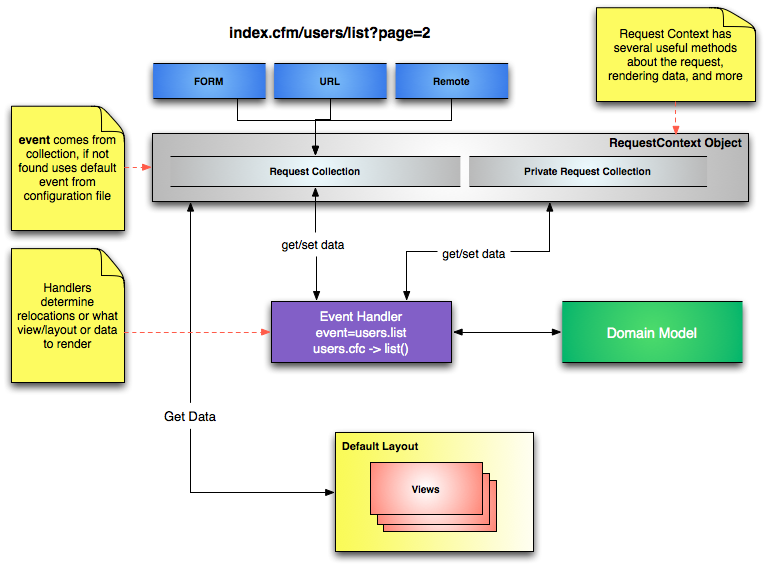
Event handlers are the controller layer in ColdBox and is what you will be executing via the URLor a FORMpost. All event handlers are singletons, which means they are cached for the duration of the application, so always remember to var scope your variables in your functions.
Tip: For development we highly encourage you to turn handler caching off or you will have to reinit the application in every request, which is annoying. Open the config/ColdBox.cfc and look for the coldbox.handlerCaching setting.
By default this is already done for you on the application templates.
Handler Code
Go open the handlers/main.cfc and let's explore the code.
Let's recap: Every action in ColdBox receives three arguments:
event- An object that models and is used to work with the current request, called the request context.rc- A struct that contains both URL/FORM variables (unsafe data)prc- A secondary struct that is private only settable from within your application (safe data)
Setting Views - Default Layout
This line event.setView( "main/index" ) in the index action told ColdBox to render a view back to the user found in views/main/index.cfm.
ColdBox also has the concept of layouts, which are essentially reusable views that can wrap up other views or layouts. They allow you to reuse content to render views/layouts inside a specific location in the CFML content. By convention, ColdBox looks for a layout called layouts/Main.cfm. This is yet another convention, the default layout. Your application can have many layouts or non-layouts at all.
Working With Incoming Data
Now, let's open the handler we created before called handlers/hello.cfc and add some public and private variables so our views can render the variables.
Let's open the view now: views/hello/index.cfm and change it to this:
Please note that we used the ColdFusion function encodeForHTML() (https://cfdocs.org/encodeforhtml) on the public variable. Why? Because you can never trust the client and what they send, make sure you use the built-in ColdFusion encoding functions in order to avoid XSS hacks or worse on incoming public (rc) variables.
If you execute the event now: http://localhost:{port}/hello/index you will see a message of Hello nobody.
Now change the incoming URL to this: http://localhost:{port}/hello/index?name=ColdBox and you will see a message of Hello ColdBox.
Tip: Please see the layouts and views section for in-depth information.
Routing Params
Now let's expect the name as part of the URL pattern; open the config/Router.cfc and let's add another route:
We use the : colon to denote incoming URL/FORM placeholder params that, if found are translated to the request collection (rc). So let's try it out: http://localhost:{port}/hello/coldbox
You can use the route() to generate the URL with params in a nice struct way:
Was this helpful?