Super Type Usage Methods
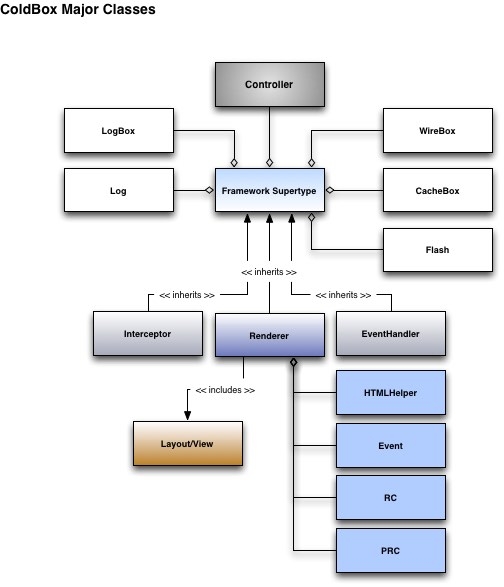
The super type offers 2 methods for interacting with your model layer:
getInstance()- Retrieve a model object (Instead of injection)populate()- Retrieve and/or populate a model object from the request collection.
Please also note that your models do not inherit from anything within ColdBox. They are shy and decoupled by default. If you need anything from the ColdBox environment, then you will have to inject it using our injection dsl.
getInstance()
getInstance()Here is the signature
Examples
populate()
populate()ColdBox can populate or bind model objects from data in the request collection by matching the name of the form element to the name of a property on the object. You can also populate model objects from JSON, XML, Queries and other structures a-la-carte by talking directly to WireBox's object populator.
Examples:
Was this helpful?