Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
This element defines custom conventions for your application. By default, the framework has a default set of conventions that you need to adhere too. However, if you would like to implement your own conventions for a specific application, you can use this setting, otherwise do not declare it:
//Conventions
conventions = {
handlersLocation = "controllers",
viewsLocation = "views",
layoutsLocation = "views",
modelsLocation = "model",
modulesLocation = "modules",
eventAction = "index"
};These are custom application settings that you can leverage in your application.
// Custom Settings
settings = {
useSkins = true,
myCoolArray = [1,2,3,4],
skinsPath = "views/skins",
myUtil = createObject("component","#appmapping#.model.util.MyUtility")
};You can read our Using Settings section to discover how to use all the settings in your application.
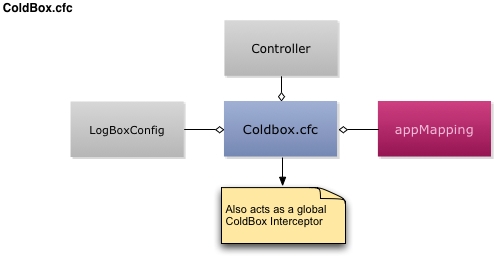
The ColdBox.cfc is the main applications' configuration object.
The ColdBox configuration CFC is the heart of your ColdBox application. It contains the initialization variables for your application and extra information used by third-party modules and ultimately how your application boots up. In itself, it is also an event listener or ColdBox Interceptor, so it can listen to life-cycle events of your application.
This CFC is instantiated by ColdBox and decorated at runtime so you can take advantage of some dependencies. Here is a table of the automatic injection this object has:
Property
Description
appMapping
The ColdBox app mapping
Once the application starts up, a reference to the instantiated configuration CFC will be stored in the configuration settings inside the ColdBox Main Controller (application.cbController) with the key coldboxConfig. You can then retrieve it later in your handlers, interceptors, modules, etc if you need to.
Another cool concept for the Configuration CFC is that it is also registered as a once the application starts up automatically for you. You can create functions that will listen to application events by simply registering them by name:
Note that the config CFC does not have the same variables mixed into it that a "normal" interceptor has. You can still access everything you need, but will need to get it from the controller in the variables scope.
This structure configures the interceptor service in your application.
//Interceptor Settings
interceptorSettings = {
throwOnInvalidStates = false,
customInterceptionPoints = "onLogin,onWikiTranslation,onAppClose"
};throwOnInvalidStatesThis tells the interceptor service to throw an exception if the state announced for interception is not valid or does not exist. Defaults to false.
customInterceptionPointsThis key is a comma delimited list or an array of custom interception points you will be registering for custom announcements in your application. This is the way to provide an observer-observable pattern to your applications.
Info Please see the section for more information.
This configuration structure is used to configure the dependency injection framework embedded in ColdBox.
binder
The location of the WireBox configuration binder to use for the application. If empty, we will use the binder in the config folder called by conventions: WireBox.cfc
singletonReload
A great flag for development. If enabled, WireBox will flush its singleton objects on every request so you can develop without any headaches of reloading.
Warning : This operation can cause some thread issues and it is only meant for development. Use at your own risk.
The CacheBox structure is based on the , and it allows you to customize the caches in your application. Below are the main keys you can fill out, but we recommend you review the CacheBox documentation for further detail.
Info : We would recommend you create a
config/CacheBox.cfcand put all your caching configuration there instead of in the main ColdBox configuration file. This will give you further portability and decoupling.
An absolute or relative path to the CacheBox configuration CFC or XML file to use instead of declaring the rest of the keys in this structure. So if you do not define a cacheBox structure, the framework will look for the default value:
The logBox structure is based on the LogBox declaration DSL, see the for much more information.
Info : If you do not define a logBox DSL structure, the framework will look for the default configuration file
config/LogBox.cfc. If it does not find it, then it will use the framework's default logging settings.
ConfigFile
You can use a configuration CFC instead of inline configuration by using this setting. The default value is config/LogBox.cfc, so by convention you can just use that location. If no values are defined or no config file exists, the default configuration file is coldbox/system/web/config/LogBox.cfc.
This directive is how you will configure the for operation. Below are the configuration keys and their defaults:
This structure allows you to define a system-wide default layout and view.
Hint Please remember that the default layout is
Main.cfm
// wirebox integration
wirebox = {
binder = 'config.WireBox',
singletonReload = true
};config/CacheBox.cfc/coldbox/system/web/config/CacheBox.cfcA structure that enables scope registration of the CacheBox factory in either server, cluster, application or session scope.
The configuration of the default cache which will have an implicit name of default which is a reserved cache name. It also has a default provider of CacheBox which cannot be changed.
A structure where you can create more named caches for usage in your CacheBox factory.
//LogBox DSL
logBox = {
// The configuration file without fileextension to use for operation, instead of using this structure
configFile = "config/LogBox",
// Appenders
appenders = {
appenderName = {
class="class.to.appender",
layout="class.to.layout",
levelMin=0,
levelMax=4,
properties={
name = value,
prop2 = value 2
}
},
// Root Logger
root = {levelMin="FATAL", levelMax="DEBUG", appenders="*"},
// Granualr Categories
categories = {
"coldbox.system" = { levelMin="FATAL", levelMax="INFO", appenders="*"},
"model.security" = { levelMax="DEBUG", appenders="console"}
}
// Implicit categories
debug = ["coldbox.system.interceptors"],
info = ["model.class", "model2.class2"],
warn = ["model.class", "model2.class2"],
error = ["model.class", "model2.class2"],
fatal = ["model.class", "model2.class2"],
off = ["model.class", "model2.class2"]
};// flash scope configuration
flash = {
// Available scopes are: session,client,cache,mock or your own class path
scope = "session",
// constructor properties for the flash scope implementation
properties = {},
// automatically inflate flash data into the RC scope at the beginning of a request
inflateToRC = true,
// automatically inflate flash data into the PRC scope at the beginning of a request
inflateToPRC = false,
// automatically purge flash data for you
autoPurge = true,
// automatically save flash scopes at end of a request and on relocations.
autoSave = true
};//Layout Settings
layoutSettings = {
// The default layout to use if NOT defined in a request
defaultLayout = "Main",
// The default view to use to render if NOT defined in a request
defaultView = "youForgot"
};The layouts array element is used to define implicit associations between layouts and views/folders, this does not mean that you need to register ALL your layouts. This is a convenience for pairing them, we are in a conventions framework remember.
Before any renderings occur or lookups, the framework will check this array of associations to try and match in what layout a view should be rendered in. It is also used to create aliases for layouts so you can use aliases in your code instead of the real file name and locations.
//Register Layouts
layouts = [
{
// The alias of a layout
name="",
// The layout file
file="",
// A list of view names to render within this layout
views="",
// A list of regex names to match a view
folders=""
}
// Examples
{ name="tester",file="Layout.tester.cfm",views="vwLogin,test",folders="tags,pdf/single" },
{ name="login",file="Login.cfm",folders="^admin/security"}
];This is an array of interceptor definitions that you will use to register in your application. The key about this array is that ORDER matters. The interceptors will fire in the order that you register them whenever their interception points are announced, so please watch out for this caveat. Each array element is a structure that describes what interceptor to register.
//Register interceptors as an array, we need order
interceptors = [
{
// The CFC instantiation path
class="",
// The alias to register in WireBox, if not defined it uses the name of the CFC
name="",
// A struct of data to configure the interceptor with.
properties={}
}
{ class="mypath.MyInterceptor",
name="MyInterceptor",
properties={useSetterInjection=false}
}
];Warning : Important: Order of declaration matters! Also, when declaring multiple instances of the same CFC (interceptor), make sure you use the name attribute in order to distinguish them. If not, only one will be registered (the last one declared).
//cachebox configuration
cachebox = {
// Location of the configuration CFC for CacheBox
configFile = "config/CacheBox.cfc",
// Scope registration for CacheBox
scopeRegistration = {enabled=true,scope=application,key=cacheBox},
// Default Cache Configuration
defaultCache = "views",
// Caches Configuration
caches = {}
};coldboxVersion
The version of the framework
controller
The ColdBox running app controller
logBoxConfig
A reference to a LogBox configuration object
getJavaSystem()
Function to get access to the java system
getSystemSetting()
Retrieve a Java System property or env value by name. It looks at properties first then environment variables
getSystemProperty()
Retrieve a Java System property value by key
getEnv()
Retrieve a Java System environment value by name
webMapping
The application's web mapping
ColdBox makes it easy to access the configuration stored in your Java system properties and your server's environment variables, even if you don't know which one it is in! Three methods are provided for your convenience:
// retrieve it
config = getSetting( 'coldboxConfig' );
// inject it
property name="config" inject="coldbox:setting:coldboxConfig";function preProcess( event, interceptData, buffer, rc, prc ){
writeDump( 'I just hijacked your app!' );abort;
}function preRender( event, interceptData, buffer, rc, prc ){
controller.getWirebox().getInstance( 'loggerService' ).doSomething();
}getEnv
( key, defaultValue )
Returns the server environment variable for key. Returns the defaultValue if it does not exist.
If you are inside config/ColdBox.cfc or a ModuleConfig.cfc or a config/WireBox.cfc you can use the three system settings functions directly! No additional work required.
If you would like to access these methods in your Application.cfc, create an instance of coldbox.system.core.delegates.Env and access them off of that component. This is required when adding a datasource from environment variables.
Example:
If you need to access these configuration values in other components, consider adding the values to your ColdBox settings and injecting the values into your other components via dependency injection.
getSystemSetting
( key, defaultValue )
Looks for key in properties first, env second. Returns the defaultValue if neither exist.
getSystemProperty
( key, defaultValue )
Returns the Java System property for key. Returns the defaultValue if it does not exist.
component {
variables.env = new coldbox.system.core.delegates.Env();
this.datasources[ "my_datasource" ] = {
driver = env.getSystemSetting( "DB_DRIVER" ),
host = env.getSystemSetting( "DB_HOST" ),
port = env.getSystemSetting( "DB_PORT" ),
database = env.getSystemSetting( "DB_DATABASE" ),
username = env.getSystemSetting( "DB_USERNAME" ),
password = env.getSystemSetting( "DB_PASSWORD" )
};
}The configuration CFC has embedded environment control and detection built-in. Environments can be detected by:
regex matching against cgi.http_host
detection of an environmental variable called ENVIRONMENT ( Coldbox 5.2 and higher )
usage of a detectEnvironment()
The first option (regex matching) is the easiest to use, but not very reliable if you are using multiple hostnames or commandbox for re-initialization.
If you are using commandbox please read ALL options below
To detect your environments you will setup a structure called environments in your coldbox configuration with the named environments and their associated regular expressions for its cgi host names to match for you automatically. If the framework matches the regex with the associated cgi.http_host, it will set a setting called Environment in your configuration settings and look for that environment setting name in your CFC as a method by convention. That's right, it will check if your CFC has a method with the same name as the environment and if it exists, it will call it for you. Here is where you basically override, remove, or add any settings according to your environment.
Warning : The environment detection occurs AFTER the
configure()method is called. Therefore, whatever settings or configurations you have on theconfigure()method will be stored first, treat those as Production settings.
The regex match will also create a global setting called "environment" which you can access and use like this:
In the above example, I declare a development key with a value list of regular expressions. If I am in a host that starts with cf2016, this will match and set the environment setting equal to development. It will then look for a development method in this CFC and execute it.
If you are using environmental variables for your different environments, you can specify an environmental variable called ENVIRONMENT and name it staging, development, testing etcetera, depending on the required environment. As in the regex example, a function named after your environment (e.g. staging() or development() ) will be called after your configure method.
If you are NOT using environmental variables you can use your own detection algorithm instead of looking at the cgi.http_host variable. You will NOT fill out an environments structure but actually create a method with the following signature:
This method will be executed for you at startup and it must return the name of the environment the application is on. You can check for any condition which distinguishes your environment from your other environments. As long as you return an environment name based on your own logic it will then store it and execute the method if it exists.
environments = {
// The key is the name of the environment
// The value is a list of regex to match against cgi.http_host
development = "^cf2016.,^lucee.,localhost",
staging = "^stg"
};if ( getSetting('environment') == 'development' ){
doSomeMajik();
}/**
* Executed whenever the development environment is detected
*/
function development(){
// Override coldbox directives
coldbox.handlerCaching = false;
coldbox.eventCaching = false;
coldbox.debugPassword = "";
coldbox.reinitPassword = "";
// Add dev only interceptors
arrayAppend( interceptors, {class="#appMapping#.interceptors.CustomLogger} );
}string public function detectEnvironment(){
}This structure within config/Coldbox.cfc is used to house module configurations. Please refer to each module's documentation on how to create the configuration structures. Usually the keys will match the name of the module to be configured.
Starting in ColdBox 7, you can store module configurations as their own configuration file within the application’s config folder outside of the config/Coldbox.cfc. The naming convention is config/modules/{moduleName}.cfc
The configuration CFC will have one configure() method that is expected to return a struct of configuration settings as you did before in the moduleSettings
The following example overrides the original module configuration entirely:
For large module configs where only a few keys need to be changed, you can update the config by modifying the struct passed in as an argument and then returning the updated version.
Just like a ModuleConfig this configuration override also gets many injections:
controller
coldboxVersion
appMapping
moduleMapping
This module configuration object will also inherit the ModuleConfig.cfc behavior that if you create methods with the same name as the environment you are on, it will execute it for you as well.
Then you can change the original struct as you see fit for that environment.
component {
function configure() {
moduleSettings = {
myModule = {
someSetting = "overridden"
}
};
}
}modulePath
logBox
log
wirebox
binder
cachebox
getJavaSystem
getSystemSetting
getSystemProperty
getEnv
appRouter
router
The modules structure is used to configure the behavior of the ColdBox Modules.
modules = {
// Will auto reload the modules in each request. Great for development but can cause some loading/re-loading issues
autoReload = true,
// An array of modules to load ONLY
include = [],
// An array of modules to EXCLUDE for operation
exclude = [ "paidModule1", "paidModule2" ]
};Danger Please be very careful when using the
autoReloadflag as module routing can be impaired and thread consistency will also suffer. This is PURELY a development flag that you can use at your own risk.
component{
function configure( original ){
return {
key : value
};
}
}component{
function configure( original ){
// override only specific keys, not the entire config
original.users.requireEmailVerification = false;
return original;
}
}function development( original ){
// add overides to the original struct
}The ColdBox directive is where you configure the framework for operation.
Info : Please note that there are no mandatory settings as of ColdBox 4.2.0. If fact, you can remove the config file completely and your app will run. It will be impossible to reinit the app however without a reinit password set.
Protect the reinitialization of the framework URL actions. For security, if this setting is omitted, we will create a random password. Setting it to an empty string will allow you to reinitialize without a password. Always have a password set for public-facing sites.
The key used in FORM or URL to reinit the framework. The default is fwreinit but you can change it to whatever you like.
Will scan the conventions directory for new handler CFCs on each request if activated. Use false for production, this is only a development true setting.
These settings map 1-1 from ColdBox events to the Application.cfc life-cycle methods. The only one that is not is the defaultEvent, which selects what event the framework will execute when no incoming event is detected via URL/FORM or REMOTE executions.
The ColdBox extension points are a great way to create federated applications that can reuse a centralized core instead of the local conventions. It is also a great way to extend some core classes with your own.
A list or array of absolute or relative paths to a UDF helper file. The framework will load all the methods found in this helper file globally. Meaning it will be injected in ALL handlers, layouts and views.
This is a location within your application or an absolute path to a cfm or bxm template that will act as your global helper for all rendered views.
A list or array of locations of where ColdBox should look for modules to load into your application. The path can be a cf mapping or cfinclude compatible location. Modules are searched and loaded in the order of the declared locations. The first location ColdBox will search for modules is the conventions folder modules
The CF include path of where to look for secondary views for your application. Secondary views look just like normal views except the framework looks in the conventions folder first and if not found then searches this location.
The CF include path of where to look for secondary layouts for your application. Secondary layouts look just like normal layouts except the framework looks in the conventions folder first and if not found then searches this location.
The CF dot notation path of where to look for secondary events for your application. Secondary events look just like normal events except the framework looks in the conventions folder first and if not found then searches this location.
The CF dot notation path of the CFC that will decorate the system Request Context object.
The CF dot notation path of the CFC that will decorate the system Controller
The event handler to call whenever ANY non-catched exception occurs anywhere in the request lifecycle execution. Before this event is fired, the framework will log the error and place the exception in the prc as prc.exception.
The event handler to call whenever a route or event is accessed with an invalid HTTP method.
This is the event handler that will fire masking a non-existent event that gets requested. This is a great place to place 302 or 404 redirects whenever non-existent events are being requested.
The relative path from the application's root level of where the custom error template exists. This template receives a key in the private request collection called exception that contains the exception. By default ColdBox does not show robust exceptions, you can turn on robust exceptions by choosing the following template:
ColdBox by convention can talk to, use and inject models from the models folder by just using their name. On startup it will scan your entire models folder and will register all the discovered models. This setting is true by default.
By default implicit views are case sensitive since ColdBox version 5.2.0, before this version the default was false.
This directive tells ColdBox that when events are executed they will be inspected for caching metadata. This does not mean that ALL events WILL be cached if this setting is turned on. It just activates the inspection mechanisms for whenever you annotate events for caching or using the runEvent() caching methods.
This is useful to be set to false in development and true in production. This tells the framework to cache your event handler objects as singletons.
Allows you to use implicit views in your application and view dispatching. You can get a performance boost if you disable this setting.
This setting allows you to configure a lambda/closure that will return back the user's request identifier according to your own algorithms. This overrides the internal way ColdBox identifies requests incoming to the application which are used internally to track sessions, flash rams, etc.
The discovery algorithm we use is the following:
If we have an identifierProvider closure/lambda/udf, then call it and use the return value
If we have sessions enabled, use the jessionId or session URL Token
If we have cookies enabled, use the cfid/cftoken
If we have in the URL the cfid/cftoken
Create a request based tracking identifier: cbUserTrackingId
This is a boolean setting used when calling the ColdBox proxy's process() method from a Flex or SOAP/REST call. If this setting is set to true, the proxy will return back to the remote call the entire request collection structure ALWAYS! If set to false, it will return, whatever the event handler returned back. Our best practice is to always have this false and return appropriate data back.
This directive tells ColdBox that when views are rendered, the cache=true parameter will be obeyed. Turning on this setting will not cause any views to be cached unless you are also passing in the caching parameters to your view() or event.setView() calls.
coldbox = {
// The name of the application
appName = "My App",
// The name of the incoming URL/FORM/REMOTE variable that tells the framework what event to execute. Ex: index.cfm?event=users.list
eventName = "event",
// The URI of the ColdBox application on the webserver. Use when ColdBox app exists within subdirectory from project root, otherwise can be omitted
appMapping = ""
};coldbox = {
reinitPassword = "h1cker",
reinitKey = "fwReinit",
handlersIndexAutoReload = true
};// reinit with no password
http://localhost/?fwreinit=1
// reinit with password
http://localhost/?fwreinit=mypasscoldbox = {
reinitKey = "myreinit"
}coldbox={
//Implicit Events
defaultEvent = "Main.index",
requestStartHandler = "Main.onRequestStart",
requestEndHandler = "Main.onRequestEnd",
applicationStartHandler = "Main.onAppInit",
applicationEndHandler = "Main.onAppEnd",
sessionStartHandler = "Main.onSessionStart",
sessionEndHandler = "Main.onSessionEnd",
missingTemplateHandler = "Main.onMissingTemplate"
}coldbox={
//Extension Points
applicationHelper = "includes/helpers/ApplicationHelper.cfm",
viewsHelper = "",
modulesExternalLocation = [],
viewsExternalLocation = "",
layoutsExternalLocation = "",
handlersExternalLocation = "",
requestContextDecorator = "",
controllerDecorator = ""
}coldbox.viewsHelper = "includes/helpers/global"coldbox = {
// Error/Exception Handling handler
exceptionHandler = "",
// Invalid HTTP method Handler
invalidHTTPMethodHandler = "",
// The handler to execute on invalid events
invalidEventHandler = "",
// The default error template
customErrorTemplate = "/coldbox/system/exceptions/BugReport-Public.cfm"
}coldbox.customErrorTemplate = "/coldbox/system/exceptions/BugReport.cfm";coldbox = {
// Persist handlers
handlerCaching = false,
// Activate event caching
eventCaching = true,
// Activate view caching
viewCaching = true,
// Return RC struct on Flex/Soap Calls
proxyReturnCollection = false,
// Activate implicit views
implicitViews = true,
// Case for implicit views
caseSensitiveImplicitViews = true,
// Auto register all model objects in the `models` folder into WireBox
autoMapModels = true,
// Your very own session tracking identifier
identifierProvider = function(){
return my own session tracking id;
}
}
The basic configuration object has 1 method for application configuration called configure() where you will place all your configuration directives and settings:
Inside of this configuration method you will place several core and third-party configuration structures that can alter your application settings and behavior. Below are the core directives you can define:
Directive
/**
* A simple CFC that configures a ColdBox application. You can even extend, compose, strategize and do your OO goodness.
*/
component{
// Mandatory configuration method
function configure(){
coldbox = {
};
}
}Type
Description
struct
An optional structure used to configure CacheBox. If not setup the framework will use its default configuration found in /coldbox/system/web/config/CacheBox.cfc
struct
The main coldbox directives structure that holds all the coldbox settings.
struct
A structure where you will configure the application convention names
struct
A structure where you will configure environment detection patterns
struct
A structure where you will configure the FlashRAM
struct
An optional structure to configure application wide interceptor behavior
array
An optional array of interceptor declarations for your application
struct
A structure where you define how the layout manager behaves in your application
array
An array of layout declarations for implicit layout-view-folder pairings in your application
struct
An optional structure to configure the logging and messaging in your application via LogBox
struct
An optional structure to configure application wide module behavior
struct
An optional structure to configure individual modules installed in your application.
struct
A structure where you can put your own application settings
struct
An optional structure used to define how WireBox is loaded